What is a power-interest grid?
A power-interest grid is a technique used to categorise stakeholders based on their power or influence and interest in a service design project. Before using the technique, you should identify all stakeholders involved. You can identify stakeholders by looking at existing documentation, holding workshops, creating ‘as is’ process maps and generally talking to people within the opportunity or area.
Why use a power-interest grid?
Categorising stakeholders in this way can allow you to develop strategies to manage all stakeholders effectively. You may use your categorisation to create a stakeholder communication plan. Stakeholders with high power and high interest will want to be engaged with regularly, whereas stakeholders with low power and low interest do not require regular and detailed communication (however, this does not necessarily mean that they should be ignored!).
What does this technique look like?
Stakeholders are plotted on the grid in relation to the power and interest they have in respect of the service design project. The grid categorises stakeholders into the following four groups:
- High power/high interest
- High power/low interest
- Low power/high interest
- Low power/low interest
You should create a grid or use a template. It is important to place the stakeholder where they actually are and not where they (or you) would like them to be. Once you have placed the stakeholder within the grid, you can look at which category they fall under and manage the stakeholder accordingly.
The complexity of the service design project will determine the detail to which you fill in the grid. For example, you might want to use more than the four positions shown below. For many service design projects, however, it is sufficient to consider the four categories below: Keep Informed, Maintain Interest, Actively Consult and Regularly Engage.
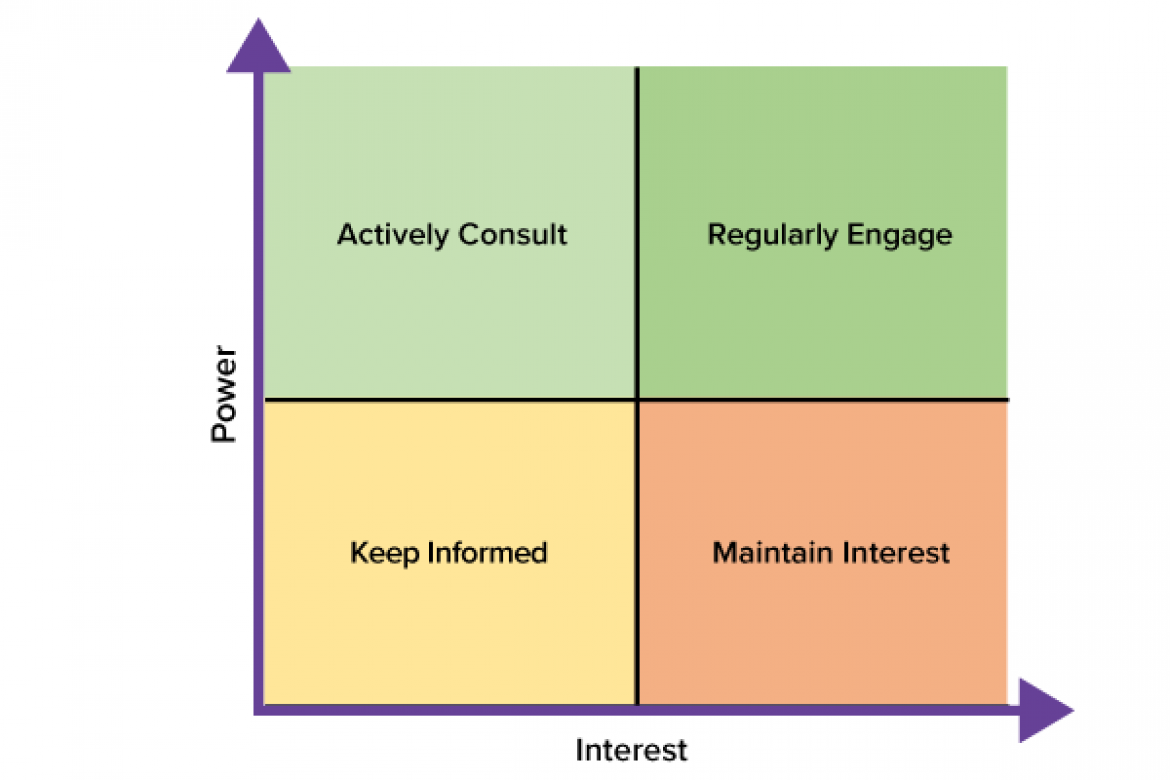
- The power/interest grid has an x axis for interest and y axis for power.
- The grid is split into four quadrants, the bottom left is keep informed; the top left is actively consult; top right is actively engage; and bottom right is maintain interest.
Who is involved?
A power-interest grid should be completed collaboratively with your service design project team.
Skills required?
- Stakeholder management – officers should be skilled in identifying and managing key stakeholders.
- Collaboration – working as part of a team to categorise stakeholders may require some negotiation or conflict resolution skills.
- Decision making – making quick and informed decisions is a skill required when categorising stakeholders.
-
The Scottish Approach to Service Design
The vision for the Scottish Approach to Service Design is that the people of Scotland are supported and empowered to actively participate in the definition, design and delivery of their public services (from policy making to live service improvement).
-
The Double Diamond (Design Council)
The Double Diamond is a visual representation of the design and innovation process. It’s a simple way to describe the steps taken in any design and innovation project, irrespective of methods and tools used.